

Story
첨단바이오 성장 포인트는
고도화 장비와 혁신적인 바이오데이터 분석
The Key Growth Points in Advanced Bio Growth Are
Sophistication Equipment and Innovative Bio Data Analysis
한양생명과학기술원 바이오공동기기센터장 최재훈 교수(생명과학과)
Professor Jae-Hoon Choi (Department of Life Science),
Director of Bio-Resource Center at Hanyang Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (HY-IBB)
- 글 김현지
- 사진 손초원
- Writing Kim Hyun-ji
- Photograph Son Cho-won
Scroll Down
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has brought digital technology and artificial intelligence into our lives, transforming many aspects. Especially in the science field, there are innovative changes that not only overcome the limitations of traditional research but are also disruptive. The biotechnology sector, now recognized as “advanced biotechnology,” is paving the way for a new future, with research scopes, methodologies, processes, and objectives entirely reimagined.

대규모 · 대용량 데이터 양산하는 첨단바이오
“바이오 기술 발전이 경제 발전에 직결된다는 판단하에 세계 각국이 첨단바이오 관련 정책을 수립하고 생명과학 분야 활성화에 나섰습니다. 최근 우리나라도 바이오 육성 정책에서 디지털바이오, 합성생물학 분야를 핵심 육성 분야로 선정했어요. 바이오 핵심 육성 분야 기초/응용 연구에 대규모 투자를 계획 중이죠. 국가 바이오 빅데이터 사업, 디지털 헬스케어 사업, 디지털바이오 데이터 활용 선도사업, 차세대 바이오파운드리 사업 등 대규모 디지털바이오 연구 투자가 예고돼 있습니다.”
한양생명과학기술원(HY-IBB) 바이오공동기기센터장을 맡고 있는 최재훈 교수는 각국 정부가 적극적으로 움직이며 바이오 분야의 디지털 전환, 첨단바이오 성장을 가속화하고 있다고 밝혔다. 기존 바이오 연구는 단일 현상이나 주제에 대한 분석을 중심으로 이뤄졌다. 이는 바이오 신기술, 신약 개발 및 상용화에 막대한 비용과 오랜 시간이 소요될 수밖에 없는 환경을 만들었다. 게다가 실패율도 높아 연구자들은 만성적인 저효율성에 고전해야 했다. 그야말로 고비용 · 저효율 구조였다. 하지만 AI, 클라우드랩, 이동형 실험실 등을 통해 자동화된 실험실과 스마트 파운드리가 도입되며 바이오 연구와 신약 개발 분야 효율성은 획기적으로 개선되고 있다.
“예전에는 단백질 한두 개, 또는 유전자(DNA)나 전사물(RNA) 한두 개를 분석하는 식으로 연구가 진행됐다면, 이제는 ‘오믹스(Omics)’ 단위로 연구가 이뤄지고 있습니다. 다양한 바이오 빅데이터가 방대한 분량으로 양산되는 겁니다. 이를 체계적으로 관리하고 효율적으로 처리하기 위해서는 바이오데이터의 디지털 전환뿐 아니라 기존보다 더욱 혁신적인 연구 체계 수립이 요구됩니다.”
오믹스란 전체를 뜻하는 말인 옴(-ome)과 학문을 뜻하는 접미사 익스(-ics)가 결합된 것이다. 여기서 나온 것이 유전체학, 전사체학, 단백질체학, 대사체학 등이다. 개별적인 유전자나 전사물, 단백질, 대사물 연구와 대비되는 개념이다. 총체적인 데이터 세트를 바탕으로 연구가 이뤄지기 때문에 대규모 · 대용량 데이터가 생성된다. 여기서 한 발 더 나아간 다중오믹스(Multi-omics)는 각각의 오믹스 데이터를 통합해서 분석한다.
“단독 연구자가 아날로그적인 방식으로 연구한다면 오믹스나 다중오믹스 분야는 성장할 수 없습니다. 최첨단 디지털 기술과 AI가 융합되기에 오믹스와 다중오믹스 연구가 활발히 이뤄지는 것이죠. 유전자, 전사물, 단백질, 대사물이 어떻게 상호작용하는지, 기존 바이오 연구로는 알 수 없었던 부분들을 더 넓은 시각으로 파악, 분석할 수 있습니다.”
최재훈 교수는 첨단바이오가 기존 바이오 연구의 한계를 뛰어넘고 있다고 말했다. 바이오 연구의 저비용 · 고효율을 실현할 뿐 아니라 새로운 발견과 성과로 인류의 삶을 바꿀 것이라 내다봤다.
Advanced Biotechnology: Generating Vast Amounts of Big Data
“Recognizing that advancements in biotechnology directly contribute to economic growth, countries worldwide are establishing policies for advanced bio and ramping up efforts to invigorate the life sciences sector. Recently, Korea has also prioritized digital biotechnology and synthetic biology as key areas in its strategy to promote biotech. The government is planning substantial investments in both basic and applied research within these crucial biotech fields. Several large-scale digital biotechnology research initiatives are on the horizon, including the projects on bio big data, digital healthcare, digital biotechnology data utilization, and next-generation biofoundry.”
Professor Jae-Hoon Choi, head of the Bio-Resource Center at Hanyang Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (HY-IBB), explained that governments worldwide are driving digital transformation and accelerating the growth of advanced biotech. Traditionally, biotechnology research has focused on analyzing individual phenomena or topics, resulting in high costs, long timelines, and frequent failures in developing new technologies, drugs, and commercialization. This created a high-cost, lowefficiency environment. However, with the introduction of automated laboratories and smart foundries powered by AI, cloud labs, and mobile laboratories, the efficiency of bio research and drug development has been greatly enhanced, leading to significant improvements in productivity and success rates.
“In the past, research typically focused on analyzing one or two proteins, genes (DNA), or transcripts (RNA). However, today, studies are conducted on an 'Omics' scale, leading to the generation of vast amounts of diverse bio big data. To manage and process this data systematically and efficiently, it is essential not only to digitally transform bio data but also to establish a more innovative research framework compared to traditional methods.”
The term “Omics” combines “ome,” meaning “whole,” with the suffix “ics,” which denotes a field of study. This has given rise to areas such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and others. Unlike studying individual genes, transcripts, proteins, or metabolites, Omics involves a broader, more comprehensive analysis. Research based on extensive data sets creates big data, and multi-omics takes it a step further by integrating and analyzing data from multiple Omics fields, offering a more holistic perspective on biological research.
“Omics and multi-omics fields cannot flourish when researchers work in isolation using outdated analog methods. The rapid growth in these areas is being fueled by the integration of advanced digital technologies and artificial intelligence. This combination enables researchers to gain a broader perspective and analyze the complex interactions between genes, transcripts, proteins, and metabolites— insights that were previously unattainable with traditional biotech approaches. This new methodology allows us to see the bigger picture and make connections that were once invisible.”
Professor Choi stated that advanced bio is surpassing the limitations of traditional bio research. He predicted that it would not only achieve low-cost, high efficiency research but also transform human lives through groundbreaking discoveries and advancements.

HY-IBB 바이오공동기기센터는 연구자-대학-산업체-정부를 아우르며 디지털바이오 융합연구 생태계 구축에 이바지할 것이다
The Hanyang Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (HY-IBB) will contribute to building a digital bio convergence research ecosystem, bridging the gap between researchers, universities, industries, and the government.
고도화된 장비, 바이오데이터 분석 역량 중요
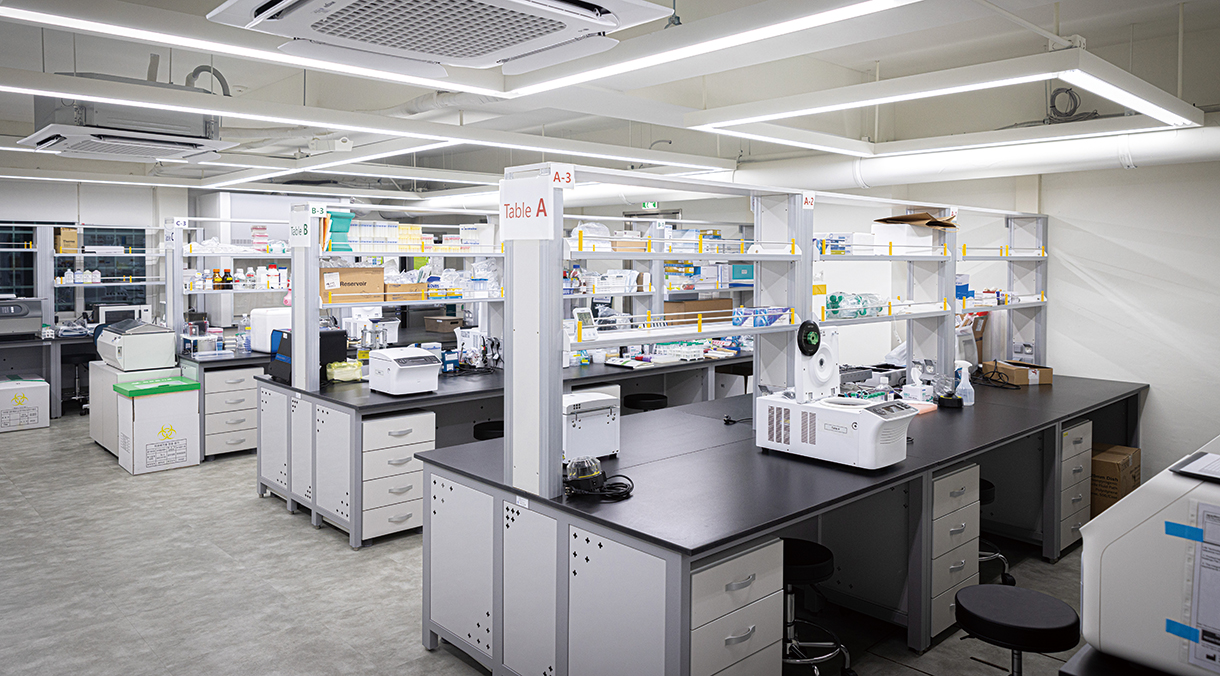
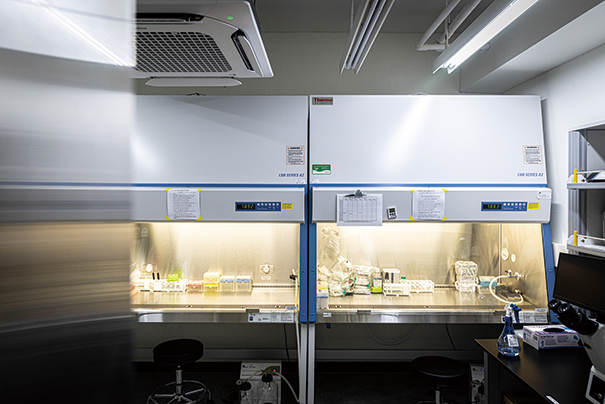
생명 · 의학 연구 발전을 위해서는 연구 장비의 집적화와 업그레이드가 필수적이다. 바이오 연구가 비약적으로 발전하고, 오믹스 및 다중오믹스 데이터 확보가 중요해짐에 따라 고도화된 첨단장비에 대한 의존도가 높아졌다. 하지만 질량분석기, 차세대 서열분석, 단일세포전사체 분석, 유세포분석기, 고해상도 공초점 레이저 주사 현미경 등 첨단바이오의 주요 장비는 개별 연구자 수준에서 구축하기 어려운 고가의 장비들이다. 대부분 억 단위인 데다 10억 원을 넘어서는 장비도 있다. 게다가 이들 첨단장비에서 양산된 대규모 · 대용량의 거대 데이터를 체계적으로 관리하고 효율적으로 분석하는 것도 쉬운 일이 아니다. 첨단장비들을 모아 연구자들이 공동으로 활용하게 하고, 바이오데이터를 통합적으로 관리하는 구심점이 필요한 이유다.
“2023년 9월부터 본격적인 연구지원 업무를 시작한 HY-IBB 바이오공동기기센터는 주요한 최첨단 바이오 장비들을 보유하고 있습니다. 또 생체시료/바이오뱅킹, 단백체, 대사체, 유전체, 이미징 등 다양한 다중오믹스 데이터 생산부터 바이오 빅데이터 통합 관리와 분석, 그리고 전산망을 통한 국가바이오스테이션 데이터 등록에 이르기까지, 바이오 전주기 과정을 꼼꼼히 지원합니다.”
최재훈 교수는 HY-IBB 바이오공동기기센터가 첨단바이오 경쟁 시대를 대비해 연구 핵심 인프라를 구축, 지원하기 위해 설립됐다고 설명했다. 데이터 기반 바이오 연구와 헬스케어 4차 산업 성장에 기여하는 것이 목표다. 센터는 △오픈랩 △유전체 코어 △생체시료 분석 코어 △이미징 코어 △BI/컴퓨팅 코어 △딥프리저(Deep Freezer) 룸 △셀컬처(Cell Culture) 룸 △생체시료 바이오뱅킹 코어 등의 시설로 구성돼 있다. 각 코어 담당교수와 장비운용연구원, 행정직원이 선정돼 있어 센터 운영의 질을 높였다. 한양대의 의과대학, 자연과학대학, 공과대학을 아우르는 다학제 간 융복합 연구 활성화에도 시너지를 미칠 것이라 기대된다.
HY-IBB 바이오공동기기센터는 지난해 교육부와 한국기초과학지원연구원 국가연구시설장비진흥센터(NFEC)가 주관한 ‘이공학학술연구기반구축(R&D) 사업 기초과학연구 역량강화사업’ 핵심연구지원센터로도 선정됐다. 이를 통해 6년간, 정부 지원과 교비를 합쳐 총 39억 원의 사업비를 지원받는다. 핵심연구지원센터로서의 이름은 ‘생체시료-다중오믹스 디지털바이오분석지원센터’다. 지난 2월 20일, 핵심연구지원센터 개소기념 심포지엄을 개최하며 본격적인 홍보에 나섰다. 국가가 지정한 핵심연구지원센터로서 생체시료 관련 다양한 오믹스 데이터를 생산하고, 디지털 전환 · 분석을 필요로 하는 바이오 연구자와 산업체를 대상으로 연구 장비 및 데이터 관리를 지원하는 데 힘쓰고 있다. 최재훈 교수는 센터 운영을 통해 연구자-대학-산업체-정부를 아우르며 디지털바이오 융합연구 생태계를 구축하는 데 이바지하겠다는 각오다.
Sophisticated Equipment and Bio Data Analysis Capabilities Are Essential
The advancement of life science and medical research requires both the integration and continuous upgrading of research equipment. With significant advances in biotechnology and the growing importance of Omics and multi-omics data, the demand for highly advanced equipment has increased. However, key instruments such as mass spectrometers, next-generation sequencing machines, single-cell transcriptome analyzers, flow cytometers, and high-resolution confocal laser scanning microscopes are prohibitively expensive for individual researchers. Many of these devices cost millions, with some exceeding ten million. Additionally, managing and efficiently analyzing the vast datasets generated by these advanced tools presents a significant challenge. This highlights the necessity of a centralized facility where researchers can share access to cutting-edge equipment and where bio data can be systematically managed and analyzed.
“Since September 2023, the HY-IBB Bio-Resource Center, which started fullfledged research support operations, possesses key state-of-the-art bio equipment. Additionally, it meticulously supports the entire bio lifecycle process, from producing various multi-omics data such as biological samples/biobanking, proteomics, metabolomics, genomics, and imaging, to integrated management and analysis of bio big data, and registration of data to the Korea BioData Station.”
Professor Choi explained that the HY-IBB Bio-Resource Center was established to build and support core research infrastructure in preparation for the era of advanced bio competition. The center aims to contribute to data-driven bio research and the growth of the fourth industrial revolution in healthcare. The facility comprises several key areas: (1) Open Lab, (2) Genomics Core, (3) Biological Sample Analysis Core, (4) Bioimaging Core, (5) Bioimaging (BI)/Computing Core, (6) Deep Freezer Room, (7) Cell Culture Room, and (8) Biological Sample Biobanking Core. The quality of the center's operations has been enhanced by appointing dedicated professors, equipment operation researchers, and administrative staff for each core area. It is expected to create synergy in promoting interdisciplinary research across Hanyang University's College of Medicine, College of Natural Sciences, and College of Engineering.
Last year, the HY-IBB Bio-Resource Center was designated as a Core Research Support Center under the “Establishment of Engineering and Science Research Infrastructure (R&D) Project: Strengthening Basic Science Research Capacity Enhancement Project,” managed by the Ministry of Education and the National Research Facilities & Equipment Center (NFEC) of the Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI). The center will receive a total of KRW 3.9 billion in funding over six years, sourced from both government support and university funds. Officially named the “Biological SampleMultiomics Digital Bioanalysis Support Center,” it held a symposium on February 20 to mark its opening and launch its promotional efforts. As a nationally designated Core Research Support Center, its mission is to generate various omics data related to biological samples and provide support to bio researchers and industries requiring digital transformation analysis with advanced research equipment and data management. Professor Choi is committed to building a digital bio-convergence research ecosystem, connecting researchers, universities, industries, and the government through the center's activities.



투자와 인내, 혜안 필요한 바이오 분야
“미국이나 유럽 등 선진국을 중심으로 첨단바이오에 많은 투자가 이뤄지고 있습니다. 바이오 분야에서 빠르게 성장하고 있는 나라는 중국입니다. 상상을 초월하는 금액의 투자가 이뤄지고 있어요. 최근에는 마리아나 해구에서 채취한 심해 생명체들의 유전체 분석 작업을 하는 것으로 알고 있습니다.”
최재훈 교수는 중국이 대대적인 투자를 단행하며 바이오 분야에 집중하고 있다고 귀띔했다. 마리아나 해구는 세계에서 가장 깊은 해저로, 태평양 북마리아나 제도의 동쪽에서 남북 방향 2550㎞ 길이로 뻗어 있는 거대 해구다. 이곳에서 발견되는 심해 생명체에 대해서는 아직 제대로 밝혀진 게 없다. 어떤 성과를 내느냐에 따라 중국이 바이오 분야 패권을 차지하게 할 무기가 될 수 있다. 최재훈 교수는 바이오 분야가 투자와 인내, 혜안이 필요하다고 강조했다.
“바이오 분야는 성과가 빠르게 나타나지 않습니다. 디지털바이오 전략을 통해 기존보다 효율적으로 연구가 진행되지만, 가치 있는 결론을 도출하기까지 짧게는 1~2년, 보통은 3~4년이 걸립니다. 10년이 넘게 걸릴 수도 있겠죠. 이런 바이오 분야의 특성을 이해하고 지속적인 투자가 이뤄져야 첨단바이오의 미래 경쟁력을 확보할 수 있습니다. 혜안을 가지고 자기주도적으로 연구에 몰입해 첨단바이오 분야에서 활약하는 한양인들이 많아지길 바랍니다.”
Biotechnology Field: A Sector Demanding Investment, Patience, and Foresight
“Advanced biotechnology is drawing significant investments, especially in developed countries such as the United States and across Europe. However, China is quickly establishing itself as a major force in the bio sector. The scale of their investment is astounding. I’ve heard they are currently conducting genomics analysis on deep-sea organisms collected from the Mariana Trench. It’s remarkable to witness how they are pushing the frontiers of biotechnology.”
Professor Choi suggested that China is making significant investments in the bio sector. The Mariana Trench, the deepest part of the world's ocean floor, spans 2,550 kilometers north to south, east of the Mariana Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Very little is known about the deep-sea organisms found there, and depending on the findings, this research could become a strategic advantage for China in the bio field. Professor Choi stressed that success in biotechnology demands investment, patience, and long-term vision.
“The bio field doesn’t produce rapid results. Although digital bio strategies have improved research efficiency, it still takes at least 1-2 years, often 3-4 years, and in some cases more than a decade to reach meaningful conclusions. Recognizing this aspect of biotechnology and maintaining steady investment is essential for securing future competitiveness in advanced bio. I hope to see more Hanyang students engage in research with foresight and self-motivation, contributing significantly to advancements in the cutting-edge bio sector.”
