

Story
불명확한 난제의 시대
융합에서 답을 찾다
Finding Answers in Convergence In an Era of Uncertainty
기술경영전문대학원 기술경영학과 김지은 교수
Prof. Kim Ji-eun, Department of Technology Management, Graduate School of Technology Management
Scroll Down
We are now living in an era that is more complex than ever. In order to overcome the problems of reality and create new opportunities, we need to properly understand the value of convergence. The world is focusing on eliminating the boundaries between fields, converging knowledge from various fields, and nurturing talents in convergence. We, too, must find answers in convergence.

생태계에서 배우는 융합!
전 세계적으로 꿀벌의 집단 실종은 큰 화제이자 걱정거리다. 국내에서도 올해 들어서만 100억 마리가량의 꿀벌이 흔적도 없이 사라졌다. 사라진 꿀벌들에 주목해야 하는 이유는 뭘까?
식물은 ‘수분(Pollination)’을 통해 생식한다. 같은 종류의 식물에서 암술과 수술의 꽃가루가 옮겨지는 과정은 자가수분(Self-Pollination), 서로 다른 그루나 다른 꽃 사이의 수분은 타가수분(Cross- Pollination)이라고 한다. 타가수분은 여러 가지 식물의 유전자를 섞어 대립 유전자의 다양성을 증가시키므로 생물 다양성을 보존하는 데 중요한 역할을 한다. 꿀벌은 전 세계 100대 작물의 70종 이상의 타가수분을 책임지는 아주 중요한 매개체다.
식물뿐 아니라 우리 사회에도 꿀벌과 타가수분이 필요하다. 하버드 경영대학원 리 플레밍 교수는 <완벽한 타가수분>(Perfecting Cross-Pollination)에서 “복잡한 현대사회의 문제를 해결하기 위해 익숙한 분야에서 벗어나, 연관이 없어 보이는 다른 분야와의 타가수분이 필수적이다”라고 강조했다. 하나의 문제를 예로 들어 보자. 범죄자의 행위를 예상해 볼 수 있을까? 이 문제에 접근하기 위해서는 화학, 생물학, 유전공학, 물리학, 공학 등 여러 과학기술을 활용한 증거 확보 방법과 심리학적 범죄자 이해 및 사회학적 인간 행동과의 연계가 필요하다. 이러한 혁신 타가수분(Innovation Cross-Pollination) 과정은 결과적으로 법과학(Forensic Science)이라는 융합학문을 탄생시켰다.
Convergence learned from the ecosystem!
The disappearance of honeybees is a big topic and a concern worldwide. In Korea, about 10 billion bees have vanished into thin air. Why should we pay attention to the disappearing bees?
Plants reproduce through pollination. The transfer of pollens between pistils and stamens of the same kind of plant is called self-pollination, and pollination among different types of plants is called cross-pollination. Cross-pollination plays a key role in preserving biodiversity as it increases allelic diversity by combining the genes of different plants. Honeybees are very important carriers for cross-pollination, as they are responsible for cross-pollination of more than 70 species among the world’s top-100 food crops.
Not only plants, but also our society need bees and cross-pollination. Professor Lee Fleming of Harvard Business School emphasizes in Perfecting Cross-Pollination, “In order to solve the complex problems of today’s society, it is essential to cross-pollinate with distant disciplines rather than with similar ones.” Let’s take a look at an example. Can a criminal’s actions be predicted? In order to approach this problem, it is necessary to link the evidence acquiring skills using various scientific technologies such as chemistry, biology, genetic engineering, physics, and engineering with psychological understanding of criminals and sociological human behavior. This innovative cross- pollination process has resulted in the birth of a new convergence discipline called forensic science.
난제와 21세기 교육 · 연구 재조명
왜 세계의 절반은 굶주리는가? 지구 온난화는 실재하는 것일까? 인공지능은 진정한 미래가 될 수 있을까?
위 질문들은 ‘U.S. 뉴스 & 월드 리포트’ 대학 랭킹에서 7년 연속 가장 혁신적인 대학으로 선정된 애리조나주립대학교 신입생들에게 주어지는 문제다. 현대사회에서 풀어야 하는 문제는 복잡하고, 재현 불가능하며, 그 범위가 넓어 단일 학문만으로 해결하기 어렵다. 디자인과 도시정책 연구학자인 리텔과 웨버는 이를 ‘불명확한 난제(Wicked Problem)’로 정의했다. 불명확한 난제는 문제의 불완전성과 복잡한 상호의존성으로 인해 문제의 한 측면을 해결하려는 노력이 다른 문제를 드러내거나 새로운 문제를 만들어내는 모순적인 구조로 되어 있다고 경고한다.
학제 간 융합연구(Interdisciplinary Research)란 이처럼 문제가 너무 광범위하거나 복잡하여 하나의 학문이나 방법으로 적절하게 다뤄지지 않는 질문에 답하거나 해결하는 과정을 의미한다. 21세기 사회, 산업, 교육 변화 움직임과 함께 주목받고 있다.
Re-examination of a wicked problem and the 21st-century education and research
Why is half of the world starving? How real is global warming? Will artificial intelligence truly be the future?
Above are the questions given to the new students at Arizona State University, which has been selected as the most innovative university in the U.S. News & World Report college ranking. The problems to be solved in the modern society are indeed so complex, unreproducible, and broad in scope that it is difficult to solve them with a single discipline. Rittel and Webber, professors of Science of Design and City Planning, defined this as a “wicked problem.” They warn that a wicked problem is in a contradicting structure in which, due to the imperfection and complex interdependence of the problem, efforts to solve one aspect of the problem reveals or creates other and new problems.
Interdisciplinary research refers to the process of answering or resolving questions that are not adequately addressed by a single discipline or method because they are too broad and/or complex. It is attracting attention with social, industrial, and educational changes in the 21st century.
좁은 범위의 융합 vs. 넓은 범위의 융합
학제 간 교육의 선구자 윌리엄 뉴웰 교수는 「학제 간 복잡성 이론」(Interdisciplinary Complexity Theory)을 통해 융합연구의 범위를 좁은 범위의 융합(Narrow Interdisciplinarity)과 넓은 범위의 융합(Wide interdisciplinarity)으로 나누어 설명한다.
융합을 요구하는 문제는 다층적인 특징을 가지며, 복잡도(Complexity)에 따라 학제 간 포괄적인 이해를 위해 학문 간의 통합(Integration)과 공통 기반(Common Ground) 형성이 필요하다. 통합은 두 개 이상의 학문이 모여 콘셉트, 가정, 방법, 이론을 서로 수정해가는 과정을 통해 동일 문제를 해결하는 것을 의미한다. 공통 기반은 상충하는 콘셉트, 가정, 방법, 이론을 통해 이뤄진다. 또 학제 간 인식론적 거리(Epistemological Distance)는 학문 분야에 따라 차이가 있는데, 물리학과 화학은 학문의 인식론적 관점에서 가까운 거리에 있는 데 반해 미술사와 수학은 비교적 멀리 떨어져 있다.
좁은 범위의 융합은 넓은 범위의 융합에 비해 발생 빈도가 높고, 융합 효과가 단기적으로 클 수 있다. 예를 들어 메카트로닉스(Mechatronics)는 기계공학(Mechanics)과 전자공학(Electronics)의 합성어로 고기능 제어를 위한 통합시스템 개발을 목표로 한다. 대표적으로 자동차 및 로봇 시스템이 메커트로닉스를 기초로 개발되었으며 제어공학, 정보공학, 전력공학 등 다양한 학문 영역을 포함하는 기술 중심의 융합이라고 볼 수 있다. 기술 중심 융합의 경우, 대부분 좁은 범위의 융합으로 전문지식을 요구하는 틈새 분야를 발견하고 2~3개의 관련 학문의 결합으로 융합이 시작된다.
반면, 넓은 범위의 융합은 학문 간 인식론적 거리가 멀며, 복잡도가 높은 사회 및 인류 공통의 문제를 다룬다. MIT 빅데이터 저널리즘, 하버드대학교 의료사회학을 그 예로 들 수 있다.
Narrow interdisciplinarity vs. wide interdisciplinarity
Professor William Newell, a pioneer in interdisciplinary education, explains, through Interdisciplinary Complexity Theory, the scope of interdisciplinarity by dividing it into narrow interdisciplinarity and wide interdisciplinarity.
Problems that require convergence have multi-layered characteristics, and according to their complexity, integration between disciplines and formation of common grounds are necessary. Integration means that two or more disciplines are used to solve one problem through the process of modifying concepts, assumptions, methods, and theories. Common ground is built through conflicting concepts, assumptions, methods, and theories. Epistemological distance between disciplines differs by the field of study. Physics and chemistry are close to each other from the epistemological point of view, whereas art history and mathematics are relatively far apart.
Narrow interdisciplinarity, compared to wide interdisciplinarity, can occur more frequently, and the results can be greater in the short term. For example, mechatronics, a compound word for mechanics and electronics, aims to develop an integrated system for high-functioning control. A representative example would be the development of automobile and robot systems based on mechatronics. It can be seen as a technologyoriented convergence that includes various academic fields such as control engineering, information engineering, and power engineering. Most technology-oriented convergence cases start by discovering a niche field that require expert knowledge of narrow interdisciplinarity and combining two or three related disciplines.
On the other hand, wide interdisciplinarity deals with problems common to society and humankind with high complexity and a far epistemological distance between disciplines. Examples include Big Data Journalism of MIT and Medical Sociology of Harvard.

4차 산업혁명 시대의 융합형 인재상
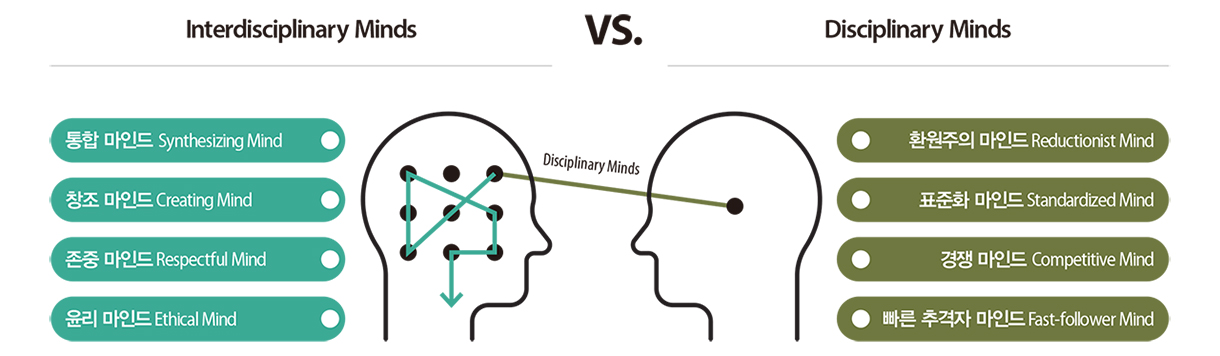
4차 산업혁명 시대의 과학사회 문제 대부분은 불명확한 난제(Wicked Problem)다. 따라서 넓은 범위의 융합을 위해서는 새로운 인재상이 요구된다. 하워드 가드너의 <미래 마인드>에서 주창하는 미래 사회에 필요한 마인드 중, 융합형 인재가 갖추어야 핵심 마인드는 다음과 같다.
- 통합 마인드 : 다양한 학문에서 필요한 정보를 선택하고 종합할 수 있는 마인드
- 창조 마인드 : 새로운 문제를 발굴하고 창의적 발상을 할 수 있는 마인드
- 존중 마인드 : 협업 과정에서 조화와 배려를 실천하는 마인드
- 윤리 마인드 : 인류와 기술의 공동 가치를 실천하는 윤리 마인드
핵심 마인드 네 가지와 반대로, 융합을 저해하는 심리학적 요인으로는 ‘전문가의 독재’라고도 이야기하는 확증 편향(Confirmation Bias)을 들 수 있다. 의사결정 과정에서 연구자가 원하는 정보만 선택적으로 모으거나, 원래 가지고 있는 생각과 신념에 상충하는 경우 정보를 무시하는 경향을 의미한다. 확증 편향은 특정 학문이나 기술에 통달한 전문성(Disciplinary Bias)에서 기인할 수 있으며, 개인 성향(Personality Bias)도 영향을 미칠 수 있다.
융합 과정에서 이러한 편향을 줄이고 초융합형 인재를 양성하기 위해서 대학은 어떻게 해야 할까? 그 답은 혁신 타가수분(Innovation Cross-Pollination)에서 찾을 수 있다.
Talents for convergence in the 4th industrial revolution era
Most of the scientific and social problems of the 4th industrial era are wicked problems. Therefore, new talents are required for wide interdisciplinarity. In the book Five Minds for the Future by Howard Gardner, the key characteristics of the mind required for convergent talent in the future society are as follows:
- The Synthesizing Mind : the ability to select and integrate information from various disciplines
- The Creating Mind : the ability to discover new problems and create ideas
- The Respectful Mind : the ability to practice harmony and consideration in collaboration
- The Ethical Mind : an ethical mind that practices the common values of humanity and technology
A psychological factor that hinders convergence, in contrast to the four key minds, is confirmation bias, which is also referred to as the “dictatorship of an expert.” It refers to the tendency of researchers to selectively collect information that they favor, or to disregard the information that contradict the beliefs and values they possess. Confirmation bias can result from a disciplinary bias in a particular discipline or technique, and personality bias can also have an influence.
What then should the universities do to reduce this bias in the convergence process and nurture super-convergent talent? The answer can be found in innovation crosspollination.

4차 산업혁명 시대의
불명확한 난제를 해결하기 위해서는
‘넓은 범위의 융합’을 실현할
새로운 융합형 인재가 필요하다
In order to solve the 'wicked problems' of the era of the 4th industrial revolution, we need new convergent talents to realize “wide interdisciplinarities.”
혁신 타가수분을 위한 대학의 변화
필자는 「광범위한 학제 간 커리큘럼의 배경 지도 작성」(Mapping the landscape of a wide interdisciplinary curriculum) 논문에서 한양대학교 교과과정 데이터를 중심으로 학문적 연결성과 대학 내 융합 가능 학과에 대해 분석한 바 있다. 연구 결과, 50%가량의 교과목이 여전히 타학과 교류 없이 사일로(Silo) 방식으로 운영되며, 평균적으로 동일 키워드의 교과목이 3~4개 학과에서 개설돼 있었다. 인접 학과 클러스터는 총 6개로 대부분 전통적인 인문과학-사회과학-공학-자연과학 등의 학제 구분을 크게 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 좁은 범위의 융합을 하는 것으로 나타났다.
그렇다면 넓은 범위의 융합은 어떻게 해야 이뤄질 수 있을까? 마이애미대학 제임스 켈리 교수는 넓은 범위의 융합을 위해서는 도전적인 문제와 함께 상충하는 가정과 방법을 가진 학문 간 연결이 필수적이라고 이야기한다. 즉, 클러스터 내(Intra-cluster)의 좁은 융합이 아닌, 클러스터 간(Inter-cluster) 연결이 시급하다.
한양대 기술경영전문대학원 전공기초 수업은 경제, 경영, 디자인, 산업공학, 수학, 컴퓨터공학, 지식재산권, 실내건축디자인 등 12명의 다른 전공 교수진이 함께하는 팀 티칭으로 운영된다. 기술경영이 요구되는 난제(예: 왜 기술 중심의 혁신이 더 이상 성공하기 어려운가? 테크노폴리(Technopoly) 시대에 필요한 기업가정신은?)를 중심으로 매주 이질적인 가정과 이론, 방법론을 도입해 문제를 재정의하고 해결하는 융합형 교과목이다. 이러한 과정은 교수와 학생 모두에게 완벽한 혁신 타가수분(Perfecting Innovation Cross-Pollination)의 기회를 제공하고 있다.
향후 넓은 범위의 융합이 활성화되기 위해서는 기존의 과학적 접근법인 축소지향적, 경쟁적, 결과 기반 마인드에서 탈피해야 한다. 나아가 학문 간 상이한 속성을 존중하고 창의적 아이디어 발상으로 연결할 수 있도록 문제 중심의 학제 개편, 유연한 교과 운영, 융합교육 평가 체계 도입 등이 필요하다. 우리 사회에 혁신 타가수분이 자리 잡도록, 대학의 혁신적 의사결정이 어느 때보다 중요한 시점이다.
Changes in universities for innovation cross-pollination
In the paper “Mapping the landscape of a wide interdisciplinary curriculum,” I have analyzed academic connectivity and departments that can be converged within the university, based on the curriculum data of Hanyang University. As a result of the study, about 50% of the courses were still operating according to the silo-method without exchanges with other departments, and courses with the same keywords were in three to four departments on average. There are a total of six clusters of related departments. Most of them show narrow interdisciplinarity within the range that does not significantly differ in traditional disciplinary classifications, such as humanities, social sciences, engineering, and natural sciences.
How, then, can a wide interdisciplinarity be achieved? Professor James Kelly at Miami University says that cross-disciplinary connections with challenging problems and contradicting assumptions and methods are essential for wide interdisciplinary convergence. In other words, we need inter-cluster connections, rather than intra-cluster connections.
Basic major classes of Hanyang University’s Graduate School of Technology Management are operated as team teaching with 12 professors from different majors such as economics, business, design, industrial engineering, mathematics, computer engineering, intellectual property, cognitive psychology, etc. It is a convergent type of curriculum that redefines and solves problems by introducing different assumptions, theories, and methodologies every week focusing on challenging problems that require technology management (e.g., Why is it difficult for technology-oriented innovations to succeed anymore? What is the entrepreneurship required in the techno-poly era?). These courses provide the perfecting innovation cross-pollination to both faculty and students.
In order to vitalize wide interdisciplinarities in the future, we need to break away from the old scientific approach, which is the reduction-oriented, competitive, and results-based mindset. Furthermore, it is necessary to reorganize the problem-centered academic system, operate a flexible curriculum, and introduce a convergence education evaluation system to respect the different natures among disciplines and to lead to creative ideas. Innovative decision-making of universities is more important than ever for innovation cross-pollination to be instilled in our society.
